Focus
Update on the Handbook on Accounting for Global Value Chains
Economic globalization has created new opportunities for businesses to organize their production chains more efficiently. This has increased the complexity of compiling economic statistics, as it is more difficult to break down production activities on a country-by-country basis. There is a need to understand the cross-country benefits and risks by being able to “look through” the global firms in the global value chains and see their contributions in the production networks of resident enterprises in multiple countries.
These emerging global production arrangements pose challenges to macroeconomic and business statistics, including the choice of the statistical unit, the classification of the (global value chain satellite) accounts, the implementation of the principle of economic control and ownership, and the recording of domestic and cross-border transactions and positions in national accounts and balance of payments statistics.
The Statistical Commission established in 2015 the Expert Group on International Trade and Economic Globalization Statistics to address these measurement challenges. The main task of this group is to develop a handbook that will address the global value chain-related classifications and the integration of the economic, environmental and social dimensions of trade and globalization, supported by an integrated framework of business and trade statistics.
The main objective of the handbook is to provide a high-level overview of how economic statistics can be made more accurate and relevant in measuring the effects of globalization in national accounts and business statistics. The handbook will provide a national perspective on globalization based on a GVC model, which describes specific GVC industries in a multi-country supply chain of goods, value adding services and institutional arrangements. Such approach will then allow for an integrated presentation of production, income, assets, liabilities, and environmental-economic transactions broken down by partner country for those GVC industries that have a significant role in the national economy resulting in GVC-specific multi-partner SUTs and related accounts.
The handbook should be helpful to a wide range of compilers in offering traditional as well as alternative solutions, such as indirect estimates using existing data as well as a mix of existing and new data sources. It should also underline that – within the overall framework – countries can flexibly (in a modular fashion) implement the recommendations according to their national priorities.
At its most recent meeting in June 2017 in Luxembourg, the expert group agreed that the GVC satellite account consisting of extended national accounts and integrated business statistics will be the central theme of the handbook and that the structure of the handbook should be amended accordingly. The group also agreed that there is a need to improve the core integrated business statistics and reduce bilateral asymmetries in their own right, as well as for purposes of GVC analysis and that the handbook should show how the GVC approach improves the relevance of core statistics.
The expert group recommended the formation of a standing group or cross-domain forum on economic statistics comprised of statisticians from national accounts, business statistics, and social and environmental statistics to study these issues in the long term. Finally, it outlined a research agenda, to include items such as: price deflators; price and volume issues; further work on classifications; development of a global groups register; the effect of digitization on GVCs and related statistics; policy relevance of GVCs; communication tools for NSOs; links to the SNA2008 research agenda; and practical application of the recommendations in the handbook.
The handbook will be finalized in 2018, circulated for global consultation and presented to the Statistical Commission at its session in 2019.
Reconciling trade asymmetries: new OECD-WTO dataset on Balanced Trade in Services (BaTIS)
High quality data on international trade in services that provide insights into the types of services that are traded, and with which partners, are vital for economic analysis and policy making. However, for many OECD and non-OECD economies, currently available trade in services statistics lack the necessary level of detail. In addition, for those countries where data are available, internal inconsistencies and in particular bilateral trade asymmetries – whereby the exports of country A to country B do not align with the imports of country B from country A – hamper the analytical and policy use of services trade statistics.
There are many reasons why the availability, quality and cross-country comparability of trade in services data are unsatisfactory, especially when compared to merchandise trade statistics. Unlike goods, which can be measured as they cross borders, services can be delivered via a variety of modes, including electronically, with typically only the financial flows relating to those transactions observable. Countries also use a variety of data sources and estimation techniques to develop trade in services statistics, and these may vary by country despite the presence of international methodological guidelines. Data confidentiality, which generates additional missing values, adds another layer of complexity.
OECD and WTO have developed a transparent methodology to create a global dataset of coherent bilateral trade in services statistics by main services categories. The approach leverages all available official data, and combines these with estimates using derivations, backcasting techniques, interpolation, and predictions derived from regression models. Exports and imports are subsequently reconciled by calculating a symmetry-index weighted average between the two, following similar approaches that have been developed in the area of merchandise trade statistics.
The first dataset is now available and covers 191 countries and partners, the 1995-2012 time period and the 11 main EBOPS 2002 categories. The accompanying methodology paper can be downloaded from both the OECD and WTO websites:http://www.oecd.org/trade/its/balanced-trade-in-services.htm and https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/trade_datasets_e.htm
The new dataset is designed to be used both for stand-alone analyses, providing a granular view on global value chains, and as input to the construction of international input-output tables such as those that underpin the OECD-WTO (TiVA) database and in regional initiatives such as the European FIGARO TiVA initiative, North American TiVA and APEC-TIVA. Further work to enlarge the number of countries and time period covered, and to reduce asymmetries in official data, including through bilateral and multilateral meetings, is under way in collaboration with national statistical offices and other international organisations. An update to the dataset with data in EBOPS 2010 up to 2016 is planned for release in 2018.
Measuring Digital Trade
Digital trade – tentatively defined as all cross-border transactions that are either digitally ordered (i.e., cross-border e-commerce), digitally facilitated (by platforms), or digitally delivered – has been growing in importance, and with it, demands for detailed statistics from a number of policy areas including market access, trade facilitation, opportunities for SMEs, regulation, competition, cross-border data flows and privacy.
In response to these policy demands, and as explicitly asked by the G20 in its Ministerial Declaration of 6-7 April 2017, the international statistics community, coordinated by the Inter-Agency Task Force on International Trade Statistics (TFITS), has prioritised and strengthened efforts to confront data gaps, biases and conceptual challenges for measuring digital trade, by developing a conceptual framework and an inventory of current measurement practices and pilot studies in more than 70 countries . This work was discussed at and supported by the OECD Working Party on Trade in Goods and Services Statistics, IMF BOPCOM and the Eurostat Balance of Payments Statistics Working Group. The TFITS also organised a first Expert Meeting on Measuring Digital Trade, which took place on 11-12 October 2017, with representatives from 18 developed and developing economies and international agencies.
Building on these inputs, the TFITS has started the development, together with experts from developed and developing countries, of a TFITS Handbook on Measuring Digital Trade, which will both elaborate the conceptual framework and address compilation practices. Given the significance and rapid developments of the topic, its potential implications and applications in developed as well developing economies, the TFITS aims to develop the Handbook expediently and plans to report on it to the UN Statistical Commission at its 2019 session.
E-learning courses on merchandise trade statistics and trade in services statistics - UNCTAD
Building on the success of their E-learning course on international trade in services statistics, finalized in 2016, UNCTAD, WTO and UNSD are in the closing stages of the elaboration of a similar on-line training for merchandise trade data, based on the IMTS-2010 concepts. The merchandise trade e-learning track, being developed in English, would be tested and validated in 2018 with a selected group of countries.
The two courses are administered by the UNCTAD's Train-for-Trade Team and they primarily target the compilers and producers of statistics. Both courses cover six training modules and are essentially structured as follows:
- statistical concepts and the importance of quality data
- institutional arrangements and other prerequisites for data collection
- data sources, collection and compilation
- metadata and quality
- dissemination and analysis, and
- new areas of work
Since it became operational in spring 2016, 398 participants from some 90 countries took the trade in services statistics e-learning training. WTO used the course as a prerequisite for the participation in two more advanced seminars they organized for LDCs', African and other developing economies' statisticians. The services E-learning modules, initially in English, will soon be available also in French.
The UNCTAD E-learning is usually organized for a group of countries based on a joint official request sent through government agencies, regional or international organizations.For information: statistics@unctad.org
ICT-enabled Services Pilot Survey - UNCTAD
In 2017, UNCTAD provided technical assistance for the launch of pilot enterprise surveys on exports of ICT-enabled services, in Costa Rica, India and Thailand. The surveys are implemented by national statistical agencies in collaboration with the private sector. The project, entirely funded by Sweden, aimed at enhancing the capacity of national agencies to produce official statistics on international trade in ICT-enabled services. A first set of preliminary results will be presented at an UNCTAD expert meeting on 28-29 November 2017 in Geneva. Lessons learned from the first round of implementation will be taken into account for revising the model survey questionnaire and methodological guidelines. A report with the main findings will be prepared by UNCTAD in 2018. Other countries have expressed an interest in conducting similar surveys. UNCTAD will look into identifying additional funding. For the purpose of the surveys, UNCTAD used concepts and definitions previously developed* with the help of the Task Force and approved by UNSC at its 47th session in 2016.**
*UNCTAD Technical Note 3 International Trade in ICT Services and ICT-enabled Services: Proposed Indicators from the Partnership on Measuring ICT for Development, available online athttp://unctad.org/en/Pages/DTL/STI_and_ICTs/ICT4D-Technical-Notes.aspx.
**Report of the Interagency Task Force on international trade statistics to the 47th Session of the UN Statistical Commission (E/CN.3/2016/24), http://unstats.un.org/unsd/statcom/47th-session/documents/2016-24-Interagency-TF-on-international-trade-statistics-E.pdf
UNCTAD-UEMOA Project on Trade in Services Statistics
This project on Trade in Services Statistics aims at improving the quality, the scope and the timeliness of the related data available in the 8 member countries of the Western Africa Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU or in French UEMOA): Benin, Burkina Faso, Cote d'Ivoire, Guinea Bissau, Mali, Niger, Senegal, Togo). The project is led by UNCTAD and the WAEMU Commission, situated in Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso), where an UNCTAD staff member is based and works directly with countries' national statistical offices (NSOs). Following the MSITS-2010 concepts, the participating agencies have developed survey questionnaires, which should be pilot-tested in each country in spring 2018. The questionnaires - available in French - cover some 70 detailed services items and aim to capture international trade in services by partner country and by GATS mode of supply (simplified approach to the modes).
Furthermore, the project provides for the development and deployment -in the WAEMU Commission and in the 8 NSOs- of an information technology system that should facilitate all stages of the statistical process: from forming samples based on existing business registers, through survey administration, data collection, compilation, aggregation and analysis, to confidentiality treatments and dissemination. Other regional groups and countries, mainly from Africa, have expressed interest in being included in this undertaking. The demands would be addressed once the project is implemented in the WAEMU region.
Technical Cooperation and Seminars
UN Comtrade Data Fair
Geneva, Switzerland, 25 September 2017
The first UN Comtrade Data Fair took place in Geneva on 25 September 2017 in cooperation with the Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies and WTO. The main objective of this one-day fair was to explain and demonstrate the latest on international trade data and their analytical use for trade-related research and policies. It was attended by over 200 users consisting of representatives from government agencies, private sector, academia, and civil society.
Eight institutes (see table below) demonstrated their applications and responded to questions throughout the day on the main exhibition floor. At lunchtime 11 major users of Comtrade data gave presentations on how they utilize trade data as well as future plans and developments. Members of the audience proceeded to break-out rooms after the lunch time panel and presenters were given the opportunity to address small focus groups for a more in-depth explanation of their applications.
The evening panel consisted of guest speakers from the ITC, the World Bank and the WTO wherein institutional perspectives were shared regarding trade data and the global value chains as they relate to analysis and policy development to promote economic integration and competitiveness in the global market.
The evening panel consisted of guest speakers from the ITC, the World Bank and the WTO wherein institutional perspectives were shared regarding trade data and the global value chains as they relate to analysis and policy development to promote economic integration and competitiveness in the global market.
For more information, visit the UN Comtrade Fair 2017.
Activities on UN Comtrade Data Fair
Geneva, Switzerland, 25 September 2017
| CEPII |
| Chatham House |
| Connecting Industries (Abrams Wiki) |
| Harvard |
| ITC |
| Oxford Economics |
| Think Blue Data |
| UNSD |
| Jürgen Abrams of Abrams Wiki |
| Charlotte Emlinger of CEPII |
| Richard King of Chatham House |
| Mans Olof-Ors of Thomson Reuters Labs and Incubator |
| Sebastian Bustos of Growth Lab, Center for International Development, Harvard |
| Paul Janecek of Think Blue Data |
| Jürgen Richtering of WTO |
| Fabienne Fortanier of OECD |
| Christian Delachenal of ITC |
| Don Brasher of Trade Data Monitor |
| Markie Muryawan of UNSD |
| Abrams Wiki |
| Globe of Economic Complexity |
| Studio Bo |
| Chatham House |
| Think Blue Data |
| UN Comtrade |
| Robert Koopman, Chief Economist of WTO |
| Marion Jansen, Chief Economist of ITC |
| José Guilherme Reis, Manager for Trade in the Trade and Competitiveness Global Practice, World Bank |
Publications and databases
UNSD

The International Trade Statistics Yearbook: Volume I – Trade by Country and Volume II - Trade by Product
- Trade by Product provide an overview of the latest trends of trade in goods and services showing country and product profiles of international trade, respectively.
And in addition, it contains several trade analytical tables on total imports and exports, external trade conversion factors, external trade indices, indicators of manufactured goods exports and fuel imports, and exports by provenance and destination.
Eurostats

Compilers Guide for statistics on Services Trade by Enterprise Characteristics (STEC)
In November 2017, Eurostat jointly with OECD published the new manual, providing recommendations on how Services Trade by Enterprise Characteristics (STEC) statistics can be compiled. The Compilers Guide for STEC is the outcome of the collaborative work of the STEC task force participants, and is a joint Eurostat-OECD Publication. It builds on the work and expertise of the Eurostat STEC Task Force, provides recommendations on how STEC statistics can be compiled. More specifically, this guide provides methodological guidance on how to produce statistics by linking different statistical datasets as STEC data are typically produced by linking International Trade in Services enterprise surveys with the Statistical Business Register. As a result additional statistical information can be derived from the existing national statistical data sources without increasing the burden to the respondents. This Eurostat-OECD Compilers Guide for Statistics on Services Trade by Enterprise Characteristics is an important tool that facilitates the production of cross-country comparable STEC statistics.
STEC statistics provide insights into how different types of enterprises – characterised for example by their main activity, size, or ownership – are engaged in international services trade. In addition to thereby providing a “profile” of services traders, STEC statistics also contribute to the larger statistical agenda on measuring economic globalization.

Globalisation patterns in EU trade and investment
Globalisation patterns in EU trade and investment highlights some aspects of economic globalisation in focusing on developments related to international trade and investment for the European Union (EU) and its 28 Member States from a business perspective, analysing exchanges between traders and patterns of behaviour within and between enterprises. It presents a broad range of statistics on the balance of payments, international trade and business in a globalised world. The first part is devoted to the role played by the European Union in global trade and investment as compared to its main trade partners. In part two, the publication focuses on the international trade in goods and services, foreign direct investment, and the structure and conduct of foreign affiliates within the EU.
OECD

OECD Statistics on International Trade in Services, Volume 2016 Issue 1
Detailed Tables by Service Category
This OECD publication includes statistics by detailed type of service on international trade in services for the 35 OECD countries, the European Union, the Euro area, Colombia and the Russian Federation.
ISBN: 9789264267008 (PDF);9789264266988(print)

OECD Statistics on International Trade in Services, Volume 2016 Issue 2
Detailed Tables by Partner Country
This OECD publication provides statistics on international trade in services by partner country for 31 OECD countries plus the European Union, the Euro area and the Russian Federation as well as links to definitions and methodological notes. The data concern trade between residents and non-residents of countries and are reported within the framework of the Manual on Statistics of International Trade in Services. This book includes summary tables of trade patterns listing the main trading partners for each country and by broad service category. Series are shown in US dollars and cover the period 2011-2015.
ISBN: 9789264267039 (PDF) ;9789264267022(print)
Overview of existing databases covering SITS
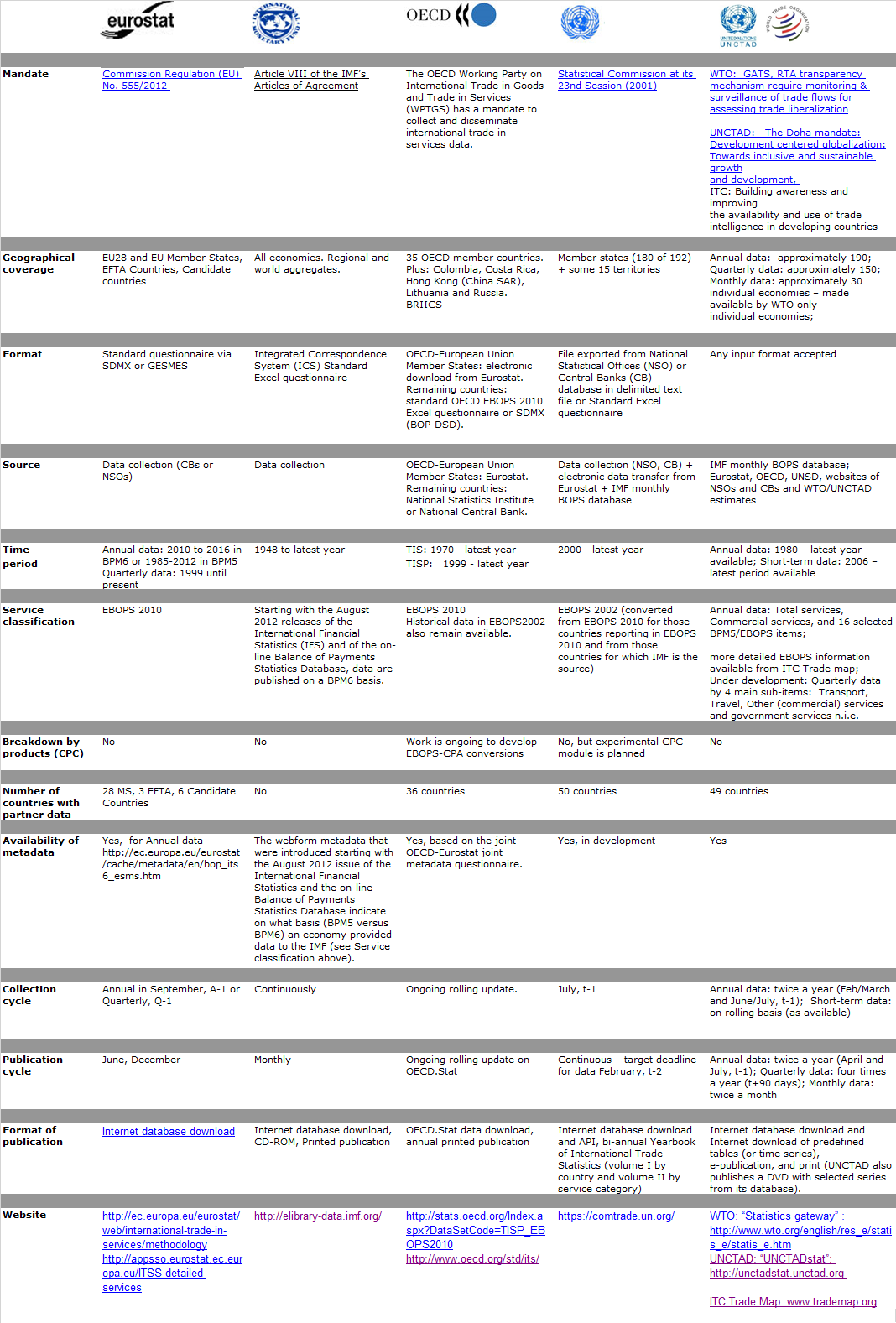
Geneva Cooperation
THE GENEVA COOPERATION: WTO-ITC-UNCTAD
The three Geneva based organizations - WTO, ITC, and UNCTAD - share the work on the compilation of annual and quarterly statistics on international trade in services. WTO, ITC, and UNCTAD make use of all available official sources, international and national, in order to build the dataset; in addition, the data gaps are filled with estimations to the extent possible. The three agencies publish the results simultaneously: four times a year for the quarterly statistics (Early-April, Mid-July, Mid-October, and Mid-January), and at the end May for the annual data.
The quarterly trade in services figures cover some 160 economies and eight principal services categories (BPM6). Starting from this data set, WTO and UNCTAD also compile and publish - in early April - the preliminary estimates of the annual trade in services for year t-1, for individual countries and several country-groups, with the partner "world".
The final complete annual figures on international trade in services, published at the end of May each year by the three Geneva cooperation agencies, cover some 200 individual economies, various country-groups, all available EBOPS-2010 services items, and partner countries (when information on partners found).
The official data, as well as UNCTAD-WTO-ITC estimates, can be viewed and downloaded here:
- UNCTADstat: http://unctadstat.unctad.org/wds/ReportFolders/reportFolders.aspx
- WTO Trade and Tariff Data: https://www.wto.org/english/res_e/statis_e/statis_e.htm
- ITC TradeMap: http://www.trademap.org/Index.aspx
The BPM6-classification data set begins with 2005 and continues until the latest year available (t-1).
The BPM5-classification statistics cover the period 1980 - 2013 and are no longer updated.
Besides, WTO maintains a monthly trade in commercial services data set (BPM6). These statistics are published for individual economies who make their monthly data available (approximately 40), the updates being posted online at WTO once a month.

UNCTAD Handbook of Statistics 2017
The new UNCTAD Handbook of Statistics is being released on 6th December 2017. This 50th edition of the handbook marks a shift from a traditional tabular publication to a shorter statistical review that emphasizes the most recent trends in international trade of goods and services, foreign direct investment, gross domestic product, commodity prices, maritime freight transport, and population.
The refurbished Handbook includes many maps, charts, and infographics, offering the possibility to seize essential messages at a glance. The accompanying texts analyze recent trends, presenting them by geographical regions, products, individual economies etc. The Handbook further includes principal economic or statistical concepts and definitions, as well as a selection of succinct statistical tables shown at the end of each of the five thematic chapters. Furthermore, the Annex presents the key economic indicators for all individual economies and various country-groups. All figures are sourced from the data sets available online at UNCTADstat. (http://unctadstat.unctad.org)

Key Statistics and Trends in International Trade 2017
This publication gives a status update on trends in international trade over the last few years. The first part gives an overview of the most recent trends and statistics. The second part provides illustrative statistics on international trade in goods and services covering the last 10 years. The second part is divided into two sections. Section 1 provides trade statistics at various levels of aggregation illustrating the evolution of trade across economic sectors and geographic regions. Section 2 presents some of the most commonly used trade indicators at the country level, so as to illustrate trade performance across countries.

Key Statistics and Trends in Trade Policy 2017
This publication informs readers on trade policy measures affecting international trade. The publication is structured in two parts. The first part discusses trade imbalances and their implications for trade policy. The second part illustrates the main trends in selected trade policy instruments by providing key descriptive statistics. The publication covers tariffs, trade agreements, non-tariff measures, trade defense measures, and exchange rates. Trends and statistics are provided at various levels of aggregation illustrating the use of the trade policy measures across economic sectors and geographic regions.
UNCTAD Non-Tariff Measures Data Collection Program (NTMs)
UNCTAD has been pioneering the collection of Non-Tariff Measures (NTM) data since the early 1990s. Nowadays, NTM statistics from some 100 economies are available, covering about 90% of the value of world trade. UNCTAD and 7 other agencies - FAO, IMF, ITC, OECD, UNIDO, WB and WTO - have been cooperating in developing an NTMs classification. A new version of the classification should be available in the first quarter of 2018.
Collecting NTM data is a sensitive task. UNCTAD provides training for data compilers and analysts in countries - particularly developing ones - to ensure comprehensiveness and accuracy of the NTM data collection. The close cooperation with national governments, local research institutes (e.g. ERIA, SIIA, CIEM), and inter-governmental bodies (e.g. ALADI, ECOWAS, SADC, EAC, COMESA) is invaluable. For more information see: UNCTAD:http://i-tip.unctad.org/Forms/TPPproject.aspx and UNCTAD/World Bank:WITS (wits.worldbank.org).
Summary of past, current and planned technical assistance activities and awareness raising relating to services trade statistics, merchandise trade statistics, Tourism statistics and Trade in Value Added statistics
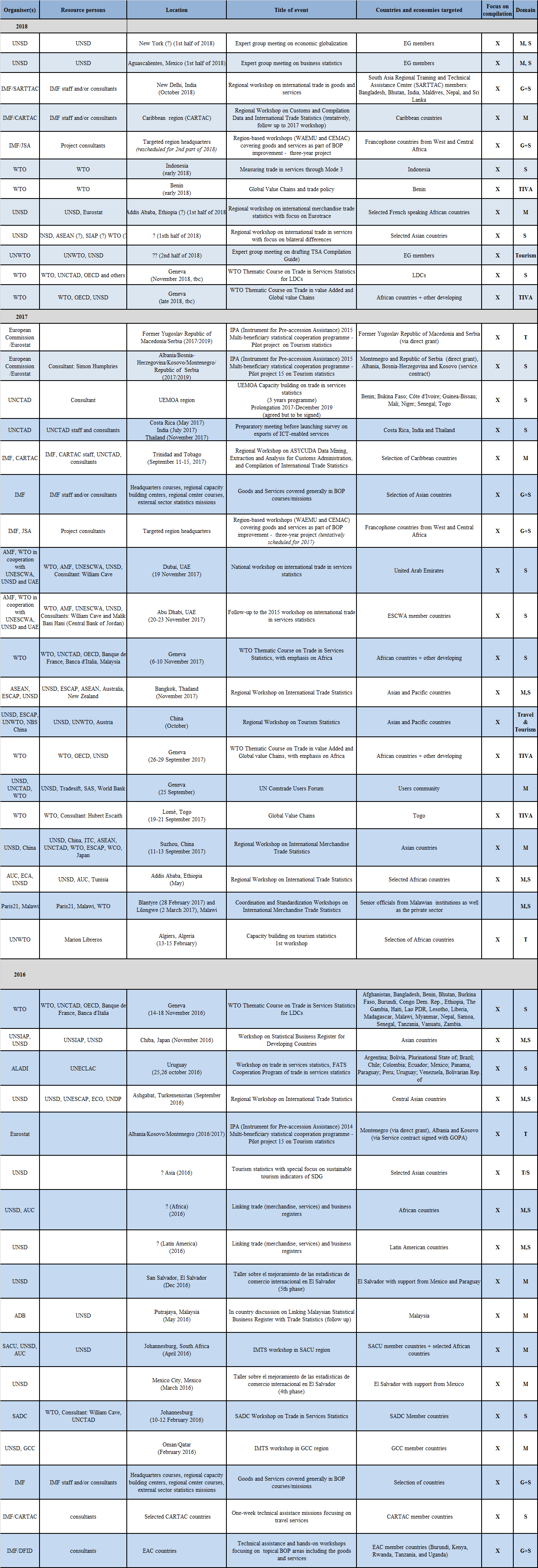
Past Events
Meeting of the Task Force on International Trade in Services (TFITS), 10-11 October 2017, Paris, Frnace
The most recent meeting of the Inter-Agency Task Force on International Trade Statistics (TFITS) took place in Paris on 10-11 October 2017. In addition to agenda items for information exchange on methodological and data quality issues related to trade statistics, as well as for updates on newly released datasets and publications, the meeting discussed bilateral trade in goods and trade in services asymmetries, the development of trade in services statistics by modes of supply, and statistical capacity building.
The TFITS meeting was followed by the TFITS Expert Meeting on Measuring Digital Trade (see more details elsewhere in this Newsletter), which brought together representatives from 18 developed and developing countries and international organisations to discuss the conceptual measurement framework for Digital Trade and share emerging compilation practices to better measure these cross-border flows.
The TFITS discussed the progress related to the reduction of bilateral trade asymmetries in services and in merchandise trade, appreciating the bilateral trade in services meetings organised by Eurostat and by OECD adjacent to their main meetings, as well as the joint work of OECD and WTO on the development of a world matrix of bilateral trade in services statistics by main EBOPS categories. The OECD also developed a balanced international merchandise trade statistics dataset. Both datasets are available online. Further updates are planned for 2018 (see also the related article on the OECD-WTO BaTIS database in this Newsletter). It was also concluded that statistical capacity building activities should further sensitise compilers to the importance of addressing asymmetries.
Important progress has been made on the development of Statistics by Modes of Supply. The TFITS discussed ongoing work by WTO and by Eurostat to develop international and European datasets on services by Mode of Supply, as well as national achievements and plans to develop such statistics.
As another strand of new statistics in international trade in services, UNCTAD presented its progress on piloting the measurement of ICT-enabled services in Costa Rica, India and Thailand, which was discussed in more detail during the Expert Group meeting on Measuring Digital Trade.
Finally, the TFITS discussed activities towards statistical capacity building, welcoming the overview produced by WTO on ongoing activities and consultants. TFITS members noted that developing country demand for technical assistance for trade in services statistics is high and growing, and considered how this demand could be met in an effective and coordinated way, e.g. via improved alignment and inclusion in National Strategies for the Development of Statistics (NSDS), developed by the Paris 21 Secretariat in cooperation with the countries. Such an inclusion would also facilitate financing of the technical capacity development activities. Hence, collaboration with Paris21was considered very important and it was agreed to improve this collaboration and coordination with the view of supporting the development of trade in services statistics.
